STEP-HFpEF & SUMMIT: Incretin analogs (semaglutide & tirzepatide) in patients with HF & ejection fraction >=45% & obesity, with or without diabetes
Semaglutide articles
STEP-HFpEF sub-analysis by baseline BMI/achieved weight loss. Nat Med 2023;2358-65
STEP-HFpEF subgroup by baseline LVEF category. JACC 2023;82:2087-96
Tirzepatide articles
Bottom line:
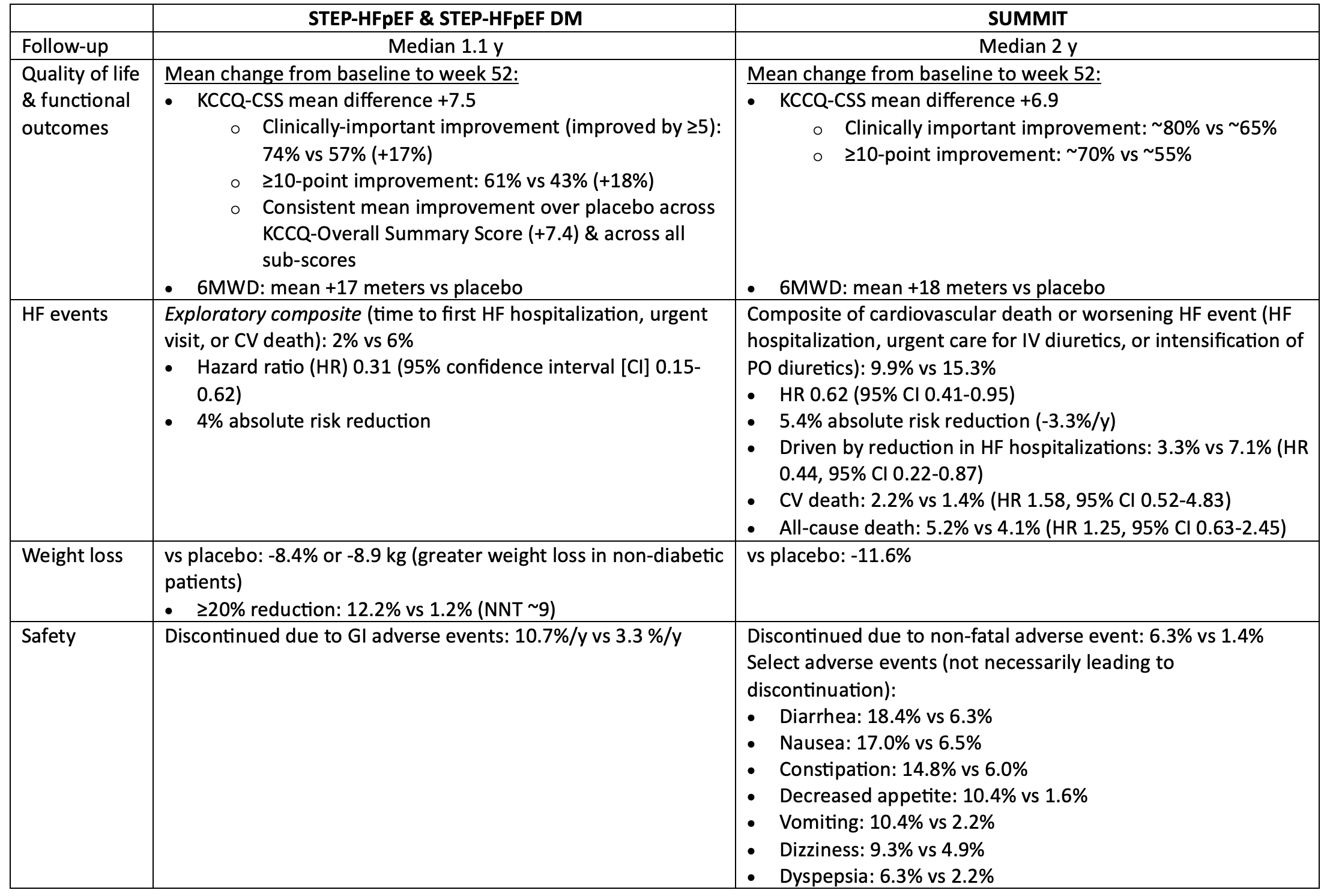
In patients with symptomatic HF, ejection fraction >=45% & BMI >=30, semaglutide & tirzepatide both improved quality of life, reduced weight, & reduced worsening HF events, but increased the risk of discontinuation due to GI intolerance.
For every 100 patients treated with semaglutide or tirzepatide for 1 year, 12-15 patients will get a noticeable improvement in their quality of life because of treatment, 3-4 will avoid a HF event, & 5-8 patients will discontinue semaglutide/tirzepatide due to intolerable side-effects (mostly gastrointestinal).
The impact of semaglutide/tirzepatide on mortality in patients with HF is unknown.
Patients
Intervention: Incretin analog (semaglutide in STEP-HFpEF trials, tirzepatide in SUMMIT)
Comparator: Matching placebo
Outcomes
Internal validity = low risk of bias
Computer-generated random sequence generation
Allocation concealment by centralized interactive web-based response system
Blinding by matching placebo & titration schedule
Intention-to-treat analysis
Low loss to follow-up (LTFU)
Generalizability & other considerations
Similar improvement (no significant treatment-subgroup interaction) in QoL with semaglutide across studied LVEF in mildly-reduced/preserved range (45% to >=60%)
In STEP-HFpEF, similar improvement in QoL with semaglutide regardless of BMI (but all ≥30), but KCCQ-CSS improvement in the semaglutide group was associated with weight loss ≥5%
Impossible to say whether lesser KCCQ improvement in patients who lost <5% body weight due to an actual cause-effect relationship between weight loss & QoL improvement, or whether this is confounded by some other factor (e.g. lower adherence to semaglutide could explain lack of both weight loss & QoL improvement)
Individual-patient-level meta-analysis of patients with HFmrEF/HFpEF in STEP-HFpEF, STEP-HFpEF-DM, SELECT, and FLOW trials are consistent with the primary outcome of SUMMIT
Reduction in HF composite (time to first worsening HF or CV death): HR 0.69 (0.53-0.89); absolute risk reduction ~0.9%/y
But no significant reduction in CV death (HR 0.82, 0.57-1.16)