Statin dose & CV events
Bottom-line:
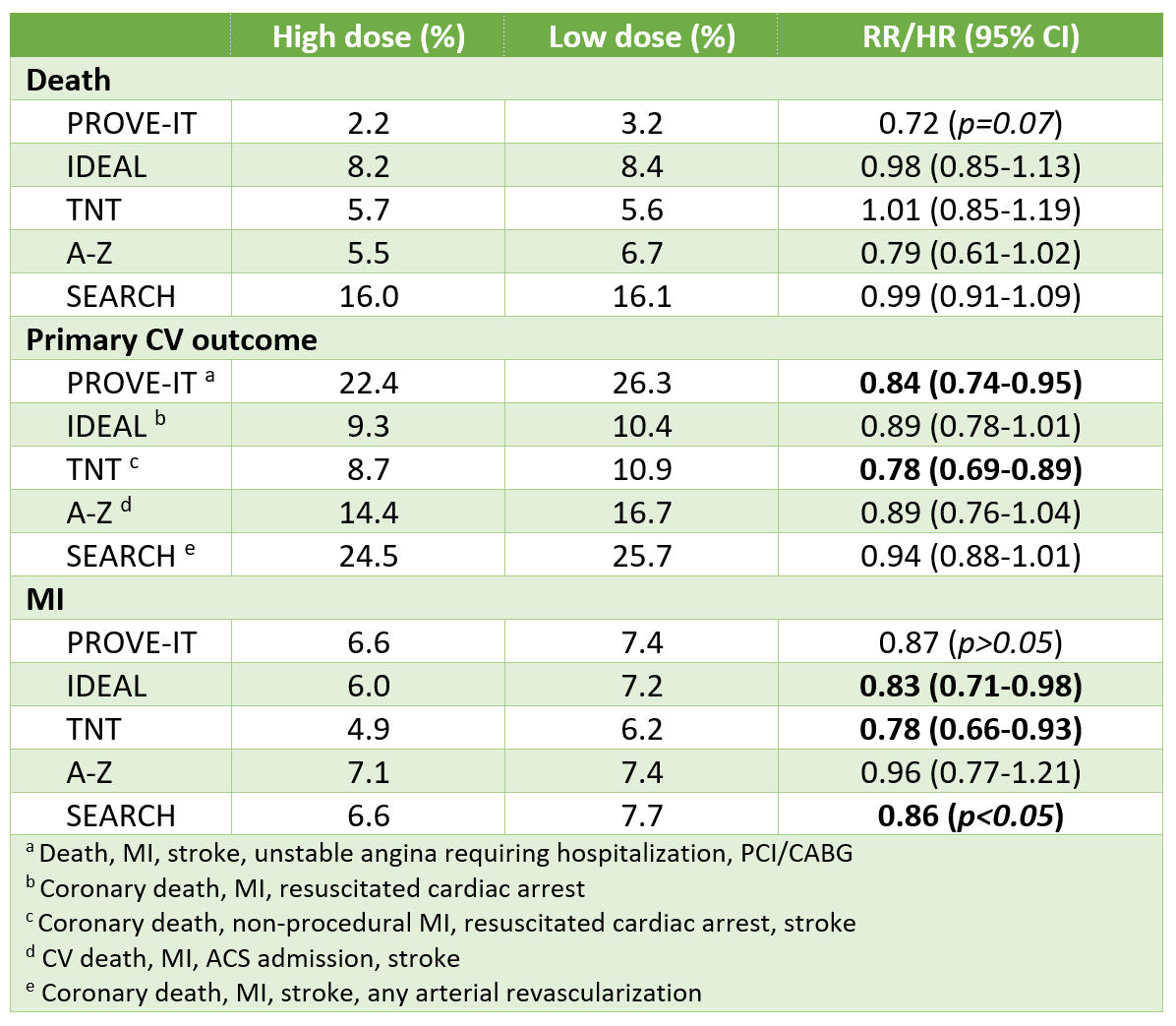
In patients with CAD, high-dose statin therapy vs low/moderate statin doses further reduces the risk of CV events by an ~15% (relative risk reduction).
In Japanese patients with CAD, moderate-dose statin reduces the risk of CV events and death versus a very low dose by ~19% (relative risk reduction).
Summary of 6 largest trials (n=52,666)
Latest trial: REAL-CAD summarized below:
- Design: RCT with open-label, blinded-outcome-adjudication design
- 13,054 randomized -> 12,413 analyzed in ITT population
- Included:
- Age 20-80 y/o +
- CAD (history of ACS, prior PCI/CABG, or angiographic coronary artery stenosis >75%) +
- LDL-C >2.6 mmol/L (excluded if LDL-C >3.0 mmol/L on pitavastatin 1 mg/d during run-in phase)
- Excluded: Known FH, contraindication to statin, HF NYHA 3-4 or LVEF <30%
- Baseline characteristics:
- Age 68 y, male 83%
- Prior MI 52% (mean 5 years ago), HF 5%, ischemic stroke 7%
- Statin before run-in: 91%, ASA 92%, ACEI/ARB 67%, beta-blocker 42%
- LDL-C: before run-in 2.4 mmol/L, after run-in on pitavastatin 1 mg/d: 2.2 mmol/L
- Interventions: Pitavastatin 4 mg/d (equivalent to ~atorvastatin 20-40 mg/d)
- Reduced LDL-C by an additional 0.4 mmol/L (18%) vs lower dose
- Control: Pitavastatin 1 mg/d (equivalent to ~atorvastatin 5 mg/d)
- Follow-up: 3.9 years (median)
Results from 5 largest RCTs
Results from REAL-CAD
- Primary outcome (CV death, MI, ischemic stroke or unstable angina requiring hospitalization):
- Higher dose 4.3%, lower dose 5.4% - 1.1% absolute risk reduction (ARR)
- HR 0.81, 95% CI 0.69-0.95
- Death: 3.3% vs 4.2% - 0.9% ARR; HR 0.81, 0.69-0.98
- MI: 0.6% vs 1.2% - 0.6% ARR; HR 0.57, 0.38-0.83
- Any muscle complaints: 1.9% vs 0.7% - 1.2% absolute risk increase
- No difference in rhabdo (<0.1%), CK increase >5xULN (0.7% vs 0.6%) or liver enzyme elevations (2.9% vs 2.7%, p=0.46)
Meta analysis comparing high- to moderate-dose statins @ mean 2.5 years
- Systematic review of 10 databases (including MEDLINE, Embase, CENTRAL) to Dec 2010
- Included 10 RCTs enrolling 41,778 patients
- Results
- Statistically significant reduction with higher dose in
- Coronary death or MI: Relative risk 0.90 (0.84-0.96), low heterogeneity (I^2=0%) in 9 trials
- Stroke (excluding TIA): RR 0.86 (0.77-0.96), I^2=0% in 10 trials
- Non-fatal MI: RR 0.82 (0.76-0.90), I^2=0% in 5 trials
- No statistically significant difference in
- Death: RR 0.92 (0.83-1.03), I^2=38% in 10 trials
- Lab abnormalities, elevated
- Liver enzymes, for ALT: RR 1.57 (1.29-1.91)
- CK: RR 2.86 (2.02-4.04)
- Subgroup analysis limited to 3 trials of patients with recent ACS (A-Z, PROVE-IT, Colivicchi et al) found possible reduction in death with higher dose (RR 0.75, p=0.005)
- Statistically significant reduction with higher dose in